Network engineers, on the surface, are just "technical laborers" who build, optimize, and troubleshoot networks, but in reality, we are the "first line of defense" in cybersecurity. A 2024 CrowdStrike report showed that global cyberattacks increased by 30%, with Chinese companies suffering losses exceeding 50 billion yuan due to cybersecurity issues. Clients don't care whether you're an operations or security specialist; when a network incident occurs, the engineer is the first to bear the blame. Not to mention the widespread adoption of AI, 5G, and cloud networks, which have made hackers' attack methods increasingly sophisticated. There's a popular post on Zhihu in China: "Network engineers who don't learn security are cutting off their own escape route!" This statement, though harsh, holds true.
In this article, I will provide a detailed analysis of eight common network attacks, from their principles and case studies to defense strategies, keeping it as practical as possible. Whether you're a newcomer or a seasoned veteran looking to advance your skills, this knowledge will give you more control over your projects. Let's get started!
No.1 DDoS Attack
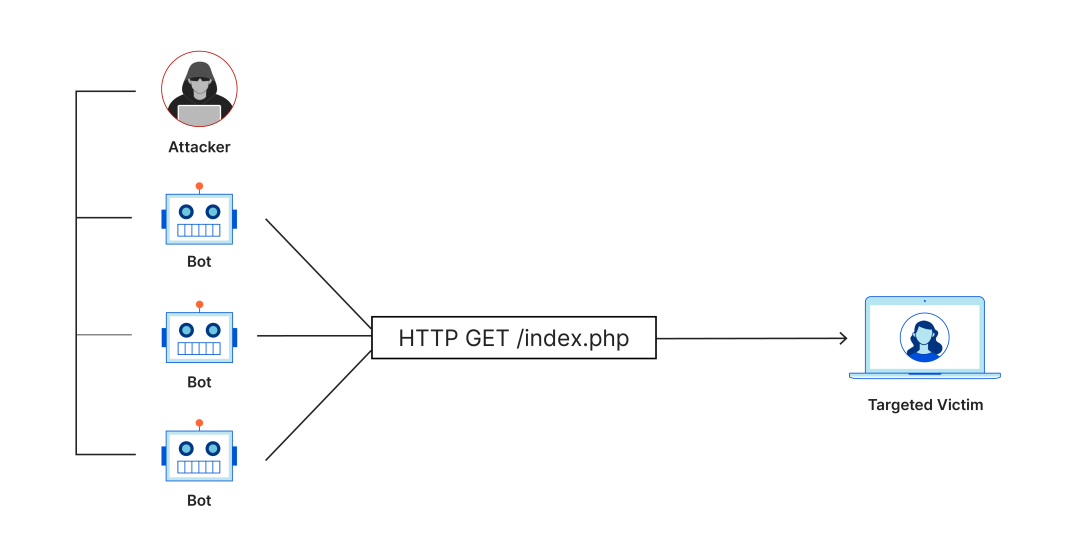
Distributed Denial-of-Service (DDoS) attacks overwhelm target servers or networks with massive amounts of fake traffic, rendering them inaccessible to legitimate users. Common techniques include SYN flooding and UDP flooding. In 2024, a Cloudflare report showed that DDoS attacks accounted for 40% of all network attacks.
In 2022, an e-commerce platform suffered a DDoS attack before Singles' Day, with peak traffic reaching 1Tbps, causing the website to crash for two hours and resulting in losses of tens of millions of yuan. A friend of mine was in charge of the emergency response and was almost driven crazy by the pressure.
How to prevent it?
○ Flow Cleaning: Deploy CDN or DDoS protection services (you may need Mylinking™ Inline Bypass Tap/Switch) to filter malicious traffic.
○ Bandwidth Redundancy: Reserve 20%-30% of bandwidth to cope with sudden traffic surges.
○ Monitoring Alarm: Use tools (you may need Mylinking™ Network Packet Broker) to monitor traffic in real time and alert on any abnormalities.
○ Emergency Plan: Cooperate with ISPs to quickly switch lines or block attack sources.
No.2 SQL Injection
Hackers inject malicious SQL code into website input fields or URLs to steal database information or damage systems. In 2023, an OWASP report stated that SQL injection remained one of the top three web attacks.
A small-to-medium-sized enterprise's website was compromised by a hacker who injected the "1=1" statement, easily obtaining the administrator's password, because the website failed to filter user input. It was later discovered that the development team hadn't implemented input validation at all.
How to prevent it?
○ Parameterized query: Backend developers should use prepared statements to avoid directly concatenating SQL.
○ WAF Department: Web application firewalls (such as ModSecurity) can block malicious requests.
○ Regular Audit: Use tools (such as SQLMap) to scan for vulnerabilities and back up the database before patching.
○ Access Control: Database users should be granted only the minimum privileges to prevent a complete loss of control.
No.3 Cross-site Scripting (XSS) Attack
Cross-site scripting (XSS) attacks steal user cookies, session IDs, and other malicious scripts by injecting them into web pages. They are categorized into reflected, stored, and DOM-based attacks. In 2024, XSS accounted for 25% of all web attacks.
A forum failed to filter user comments, allowing hackers to insert script code and steal login information from thousands of users. I've seen cases where clients were extorted for CNY500,000 yuan because of this.
How to prevent it?
○ Input filtering: Escape user input (such as HTML encoding).
○ CSP Strategy: Enable content security policies to restrict script sources.
○ Browser protection: Set HTTP headers (such as X-XSS-Protection) to block malicious scripts.
○ Tool Scan: Use Burp Suite to regularly check for XSS vulnerabilities.
No.4 Password Cracking
Hackers obtain user or administrator passwords through brute-force attacks, dictionary attacks, or social engineering. A 2023 Verizon report indicated that 80% of cyber intrusions were related to weak passwords.
A company's router, using the default password "admin," was easily logged into by a hacker who implanted a backdoor. The engineer involved was subsequently fired, and the manager was also held accountable.
How to prevent it?
○ Complex Passwords: Force 12 or more characters, mixed case, numbers, and symbols.
○ Multi-factor Authentication: Enable MFA (such as SMS verification code) on critical equipment.
○ Password Management: Use tools (such as LastPass) to manage centrally and change them regularly.
○ Limit Attempts: The IP address is locked after three failed login attempts to prevent brute-force attacks.
No.5 Man-in-the-middle Attack (MITM)
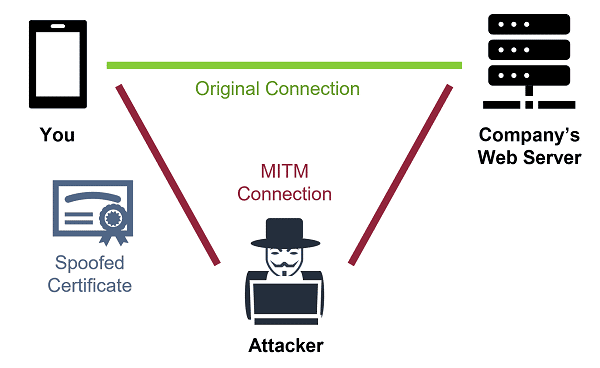
Hackers intervene between users and servers, intercepting or tampering with data. This is common in public Wi-Fi or unencrypted communications. In 2024, MITM attacks accounted for 20% of network sniffing.
A coffee shop's Wi-Fi was compromised by hackers, resulting in users losing tens of thousands of dollars when their data was intercepted while logging into a bank's website. Engineers later discovered that HTTPS was not being enforced.
How to prevent it?
○ Force HTTPS: The website and API are encrypted with TLS, and HTTP is disabled.
○ Certificate Verification: Use HPKP or CAA to ensure the certificate is trustworthy.
○ VPN Protection: Sensitive operations should use VPN to encrypt traffic.
○ ARP protection: Monitor the ARP table to prevent ARP spoofing.
No.6 Phishing Attack
Hackers use spoofed emails, websites, or text messages to trick users into revealing information or clicking on malicious links. In 2023, phishing attacks accounted for 35% of cybersecurity incidents.
An employee of a company received an email from someone claiming to be their boss, requesting a money transfer, and ended up losing millions. It was later discovered that the email domain was fake; the employee hadn't verified it.
How to prevent it?
○ Employee Training: Regularly conduct cybersecurity awareness training to teach how to identify phishing emails.
○ Email Filtering: Deploy an anti-phishing gateway (such as Barracuda).
○ Domain Verification: Check the sender's domain and enable the DMARC policy.
○ Double Confirmation: Sensitive operations require verification by phone or in person.
No.7 Ransomware
Ransomware encrypts victims' data and demands a ransom for decryption. A 2024 Sophos report indicated that 50% of businesses worldwide had experienced ransomware attacks.
A hospital's network was compromised by LockBit ransomware, causing system paralysis and the suspension of surgeries. Engineers spent a week recovering the data, incurring significant losses.
How to prevent it?
○ Regular Backup: Off-site backup of critical data and testing of the recovery process.
○ Patch Management: Update systems and software promptly to plug vulnerabilities.
○ Behavioral Monitoring: Use EDR tools (such as CrowdStrike) to detect anomalous behavior.
○ Isolation Network: Segmenting sensitive systems to prevent the spread of viruses.
No.8 Zero-day Attack
Zero-day attacks exploit undisclosed software vulnerabilities, making them extremely difficult to prevent. In 2023, Google reported the discovery of 20 high-risk zero-day vulnerabilities, many of which were used for supply chain attacks.
A company using SolarWinds software was compromised by a zero-day vulnerability, affecting its entire supply chain. Engineers were helpless and could only wait for a patch.
How to prevent it?
○ Intrusion Detection: Deploy IDS/IPS (such as Snort) to monitor abnormal traffic.
○ Sandbox Analysis: Use a sandbox to isolate suspicious files and analyze their behavior.
○ Threat Intelligence: Subscribe to services (such as FireEye) to get the latest vulnerability information.
○ Least Privileges: Restrict software permissions to reduce the attack surface.
Fellow network members, what kinds of attacks have you encountered? And how did you handle them? Let's discuss this together and work together to make our networks even stronger!
Post time: Nov-05-2025