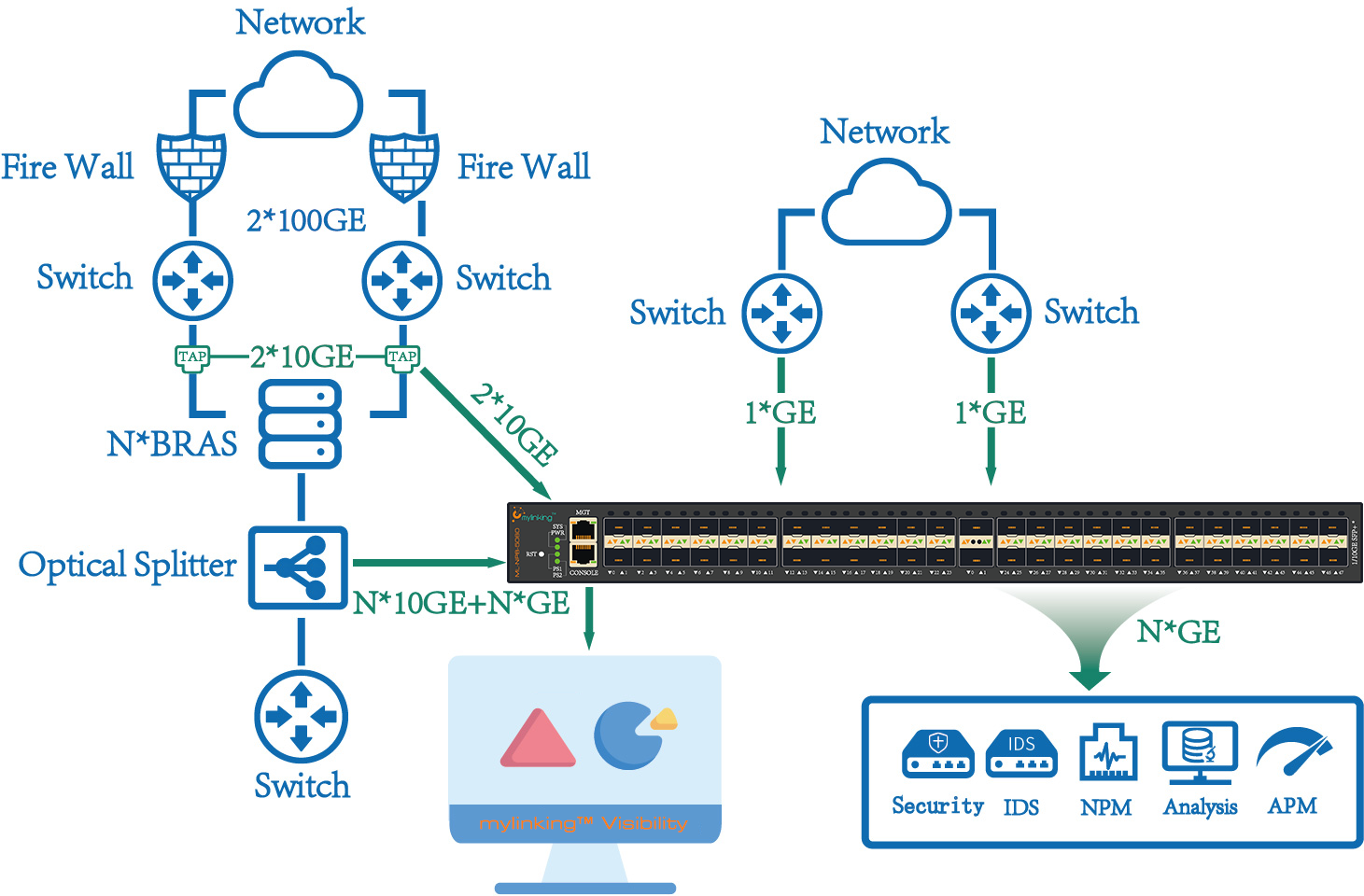
SPAN
You can use the SPAN function to copy packets from a specified port to another port on the switch that is connected to a network monitoring device for network monitoring and troubleshooting.
SPAN does not affect the packet exchange between the source port and the destination port. All packets entering and outputting from the source port are copied to the destination port. However, if the mirrored traffic exceeds the bandwidth of the destination port, for example, if the 100Mbps destination port monitors the traffic of the 1000Mbps source port, packets may be discarded
RSPAN
Remote port mirroring (RSPAN) is the extension of local port mirroring (SPAN). Remote port mirroring breaks the restriction that the source port and destination port must be on the same device, enabling the source port and destination port to span multiple network devices. In this way, the network administrator can sit in the central equipment room and observe the data packets of the remote mirrored port through the analyzer.
RSPAN transmits all mirrored packets to the destination port of the Remote mirroring device through a special RSPAN VLAN(called the Remote VLAN) The roles of devices fall into three categories:
1) Source Switch: Remote image source port of switch, is responsible for a copy of the source port message from a source switch output port output, through the Remote VLAN forwarding, transmit to the middle or to switch.
2) Intermediate Switch: in the network between the source and destination switch, switch, mirror through Remote VLAN packet transmission to the next or to switch in the middle. If the source switch is directly connected to the destination switch, no intermediate switch exists.
3) Destination Switch: Remote mirror destination port of switch, mirror from Remote VLAN to receive a message through the mirror destination port forwarding to monitor equipment.
ERSPAN
Encapsulated Remote port mirroring (ERSPAN) is an extension of remote port mirroring (RSPAN). In a common remote port mirroring session, mirrored packets can be transmitted only at Layer 2 and cannot pass through a routed network. In an encapsulated remote port mirroring session, mirrored packets can be transmitted between routed networks.
ERSPAN encapsulates all mirrored packets into IP packets through a GRE tunnel and routes them to the destination port of the remote mirroring device. The roles of each device are divided into two categories:
1) Source Switch: encapsulation remote image source port of switch, is responsible for a copy of the source port message from a source switch output port output, through the GRE encapsulated into the IP packet forwarding, transfer switches to purpose.
2) Destination Switch: encapsulation remote mirror destination port of switch, will receive the message through the mirror mirror destinationport, after decapsulation GRE message forwarded to monitor equipment.
To implement the remote port mirroring function, IP packets encapsulated by GRE must be routable to the destination mirroring device on the network

Packet Encapsulation output
Supported to encapsulate any specified packets in the captured traffic to the RSPAN or ERSPAN header and output the packets to the back-end monitoring system or network switch

Tunnel Packet Termination
Supported the tunnel packet termination function, which can configure IP addresses, masks, ARP responses, and ICMP responses for traffic input ports. Traffic to be collected on the user network is directly sent to the device through tunnel encapsulation methods such as GRE, GTP, and VXLAN
VxLAN, VLAN, GRE, MPLS Header Stripping
Supported the VxLAN, VLAN, GRE, MPLS header stripped in the original data packet and forwarded output.
Post time: Jan-03-2023