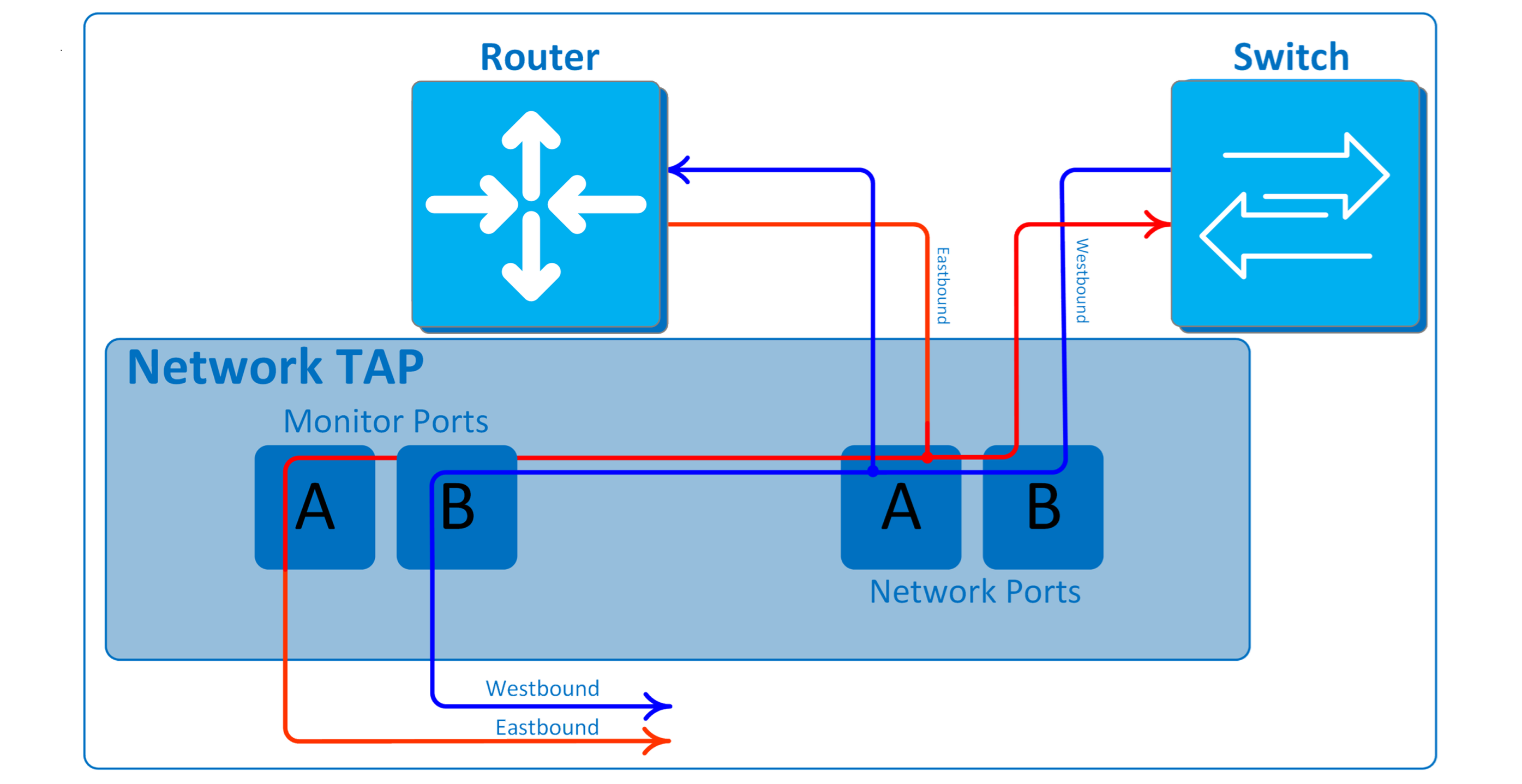
TAPs (Test Access Points), also known as also known as Replication Tap, Aggregation Tap, Active Tap, Copper Tap, Ethernet Tap, Optical Tap, Physical Tap, etc. Taps are a popular method for acquiring network data. They provide comprehensive visibility into network data flows and accurately monitor bidirectional conversations at full line speed, without packet loss or latency. The emergence of TAPs has revolutionized the field of network monitoring and surveillance, fundamentally changing the access methods for monitoring and analysis systems and providing a complete and flexible solution for the entire monitoring system.
Current technological developments have produced a wide variety of tap types: taps that aggregate multiple links, regeneration taps that split a link's traffic into several parts, bypass taps, and matrix tap switches.
Currently, the more popular Tap brands in the industry include NetTAP and Mylinking, among which Mylinking is recognized as an excellent Tap and NPB brand in the Chinese industry, with a high market share, stability and good performance.
Advantages of TAP
1. Capture 100% of the data packets without any packet loss.
2. Irregular data packets can be monitored, facilitating troubleshooting.
3. Accurate timestamps, no delays and retiming.
4. One-time installation makes it easy to connect and move the analyzer.
Disadvantages of TAP
1. You need to spend extra money to purchase a splitter TAP, which is expensive and takes up rack space.
2. Only one link can be viewed at a time.
Typical Applications of TAP
1. Commercial links: These links require extremely short troubleshooting times. By installing TAPs in these links, network engineers can quickly locate and troubleshoot sudden problems.
2. Core or backbone links. These have high bandwidth utilization and cannot be interrupted when connecting or moving the analyzer. TAP ensures 100% data capture without packet loss, providing performance assurance for accurate analysis of these links.
3. VoIP and QoS: VoIP quality of service testing requires accurate jitter and packet loss measurements. TAPs fully guarantee these tests, but mirrored ports can alter jitter values and provide unrealistic packet loss rates.
4. Troubleshooting: Ensure that irregular and erroneous data packets are detected. Mirrored ports will filter out these packets, preventing engineers from providing important and complete data information for troubleshooting.
5. IDS application: IDS relies on complete data information to identify intrusion patterns, and TAP can provide reliable and complete data streams to the intrusion detection system.
6. Server cluster: The multi-port splitter can connect 8/12 links at the same time, enabling remote and free switching, which is convenient for monitoring and analysis at any time.
SPAN (Switch Port Analysis) is also known as a Mirrored Port or Port Mirror. Advanced switches can copy data packets from one or more ports to a designated port, called a "mirror port" or "destination port." An analyzer can connect to the mirrored port to receive data. However, this feature can affect switch performance and cause packet loss when data is overloaded.
Advantages of SPAN
1. Economical, no additional equipment required.
2. All traffic on a VLAN on a switch can be monitored simultaneously.
3. One analyzer can monitor multiple links.
Disadvantages of SPAN
1. Mirroring traffic from multiple ports to one port can cause cache overload and packet loss.
2. Packets are retimed as they pass through the cache, making it impossible to accurately determine time scales such as jitter, packet interval analysis, and latency.
3. Unable to monitor OSI layer 1.2 error packets. Most data mirroring ports filter out irregular data packets, which cannot provide detailed and useful data information for troubleshooting.
4. Because the traffic of the mirrored port increases the CPU load of the switch, it will cause the switch's performance to decline.
Typical Applications of SPAN
1. For links with low bandwidth and good mirroring capabilities, multi-port mirroring can be used for flexible analysis and monitoring.
2. Trend monitoring: When precise monitoring is not required, only irregular data statistics are sufficient.
3. Protocol and application analysis: relevant data information can be provided conveniently and economically from a mirror port
4. Entire VLAN monitoring: Multi-port mirroring technology can be used to easily monitor the entire VLAN on a switch.
Introduction to VLAN:
First, let's introduce the basic concept of a broadcast domain. This refers to the range within which broadcast frames (destination MAC addresses are all 1) can be transmitted, and in other words, the range within which direct communication is possible. Strictly speaking, not only broadcast frames, but also multicast frames and unknown unicast frames can travel freely within the same broadcast domain.
Originally, a Layer 2 switch could only establish a single broadcast domain. On a Layer 2 switch without any VLANs configured, any broadcast frame would be forwarded to all ports except the receiving port (flooding). However, using VLANs allows a network to be segmented into multiple broadcast domains. VLANs are the technology used to segment broadcast domains on Layer 2 switches. By utilizing VLANs, we can freely design the composition of broadcast domains, increasing the flexibility of network design.
Post time: Sep-04-2025