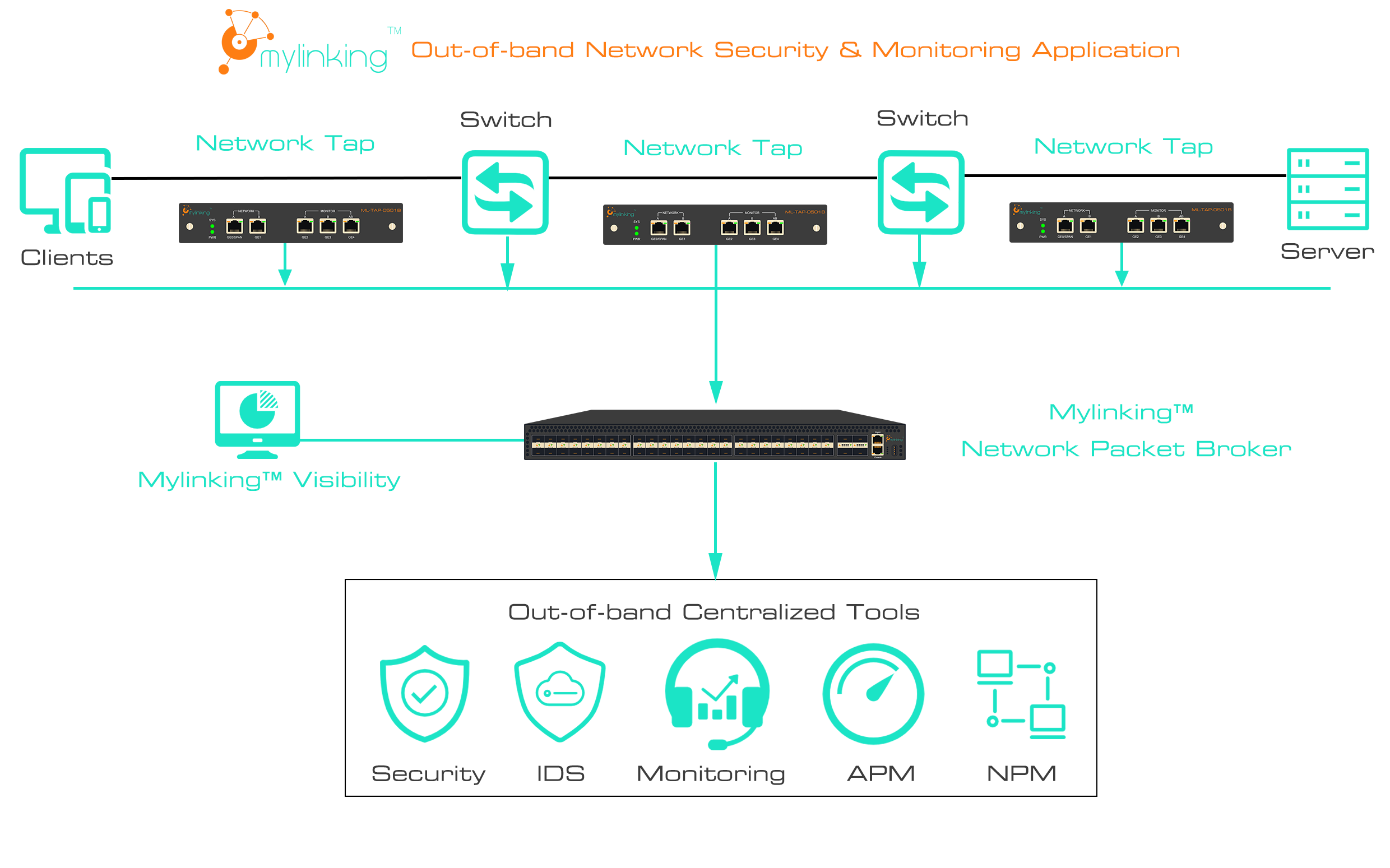
Intrusion Detection System (IDS) is like the scout in the network, the core function is to find the intrusion behavior and send an alarm. By monitoring network traffic or host behavior in real time, it compares the preset "attack signature library" (such as known virus code, hacker attack pattern) with "normal behavior baseline" (such as normal access frequency, data transmission format), and immediately triggers an alarm and records a detailed log once an anomaly is found. For example, when a device frequently tries to brute force crack the server password, IDS will identify this abnormal login pattern, quickly send warning information to the administrator, and retain key evidence such as the attack IP address and the number of attempts to provide support for subsequent traceability.
According to the deployment location, IDS can be mainly divided into two categories. Network IDS (NIDS) are deployed at key nodes of the network (e.g., gateways, switches) to monitor the traffic of the entire network segment and detect cross-device attack behavior. Mainframe IDS (HIDS) are installed on a single server or terminal, and focus on monitoring the behavior of a specific host, such as file modification, process startup, port occupancy, etc., which can accurately capture the intrusion for a single device. An e-commerce platform once found abnormal data flow through NIDS -- a large number of user information was being downloaded by unknown IP in bulk. After timely warning, the technical team quickly locked the vulnerability and avoided data leakage accidents.
Mylinking™ Network Packet Brokers application in Intrusion Detection System (IDS)
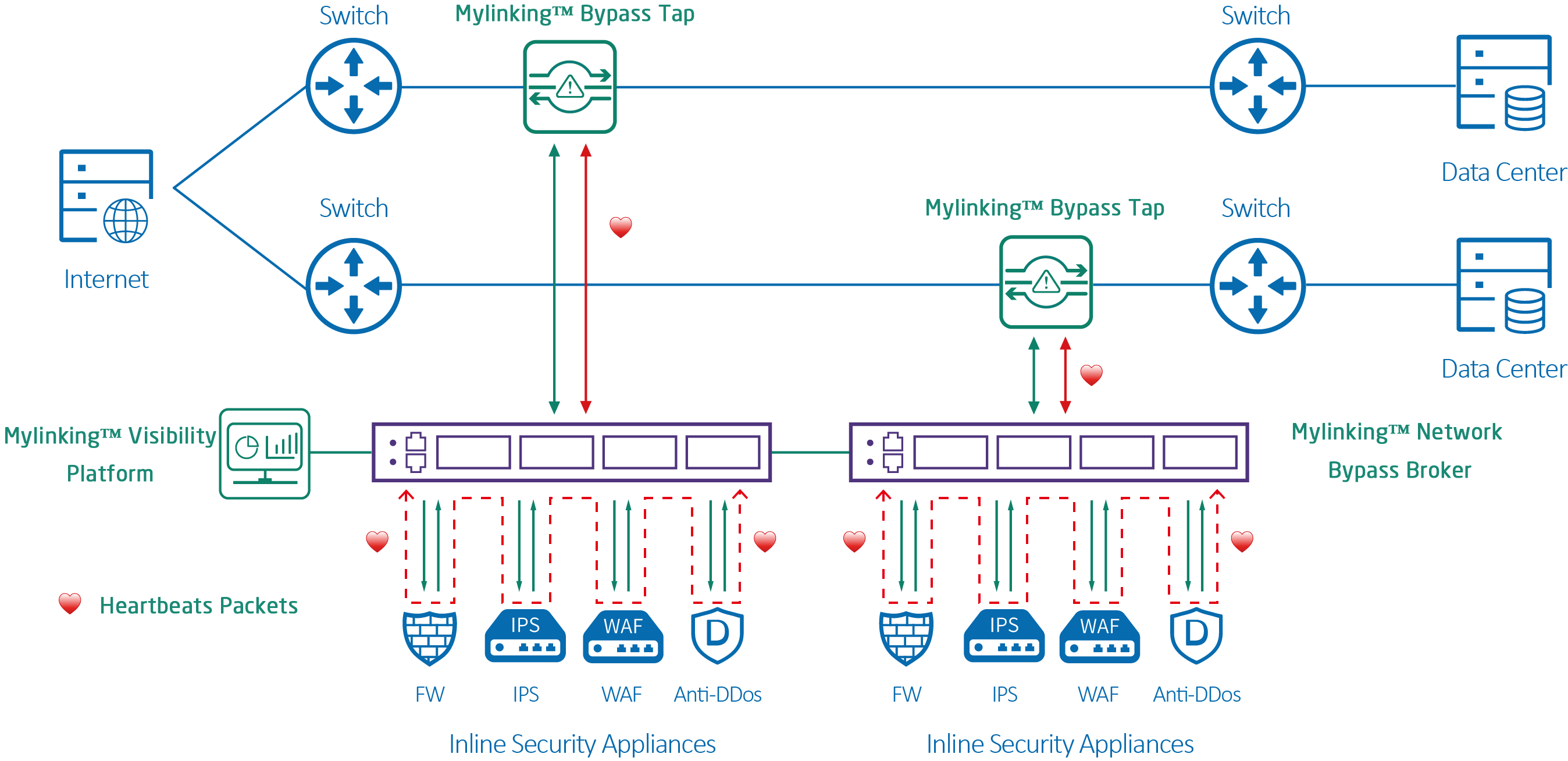
Intrusion Prevention System (IPS) is the "guardian" in the network, which increases the ability of actively intercepting attacks on the basis of the detection function of IDS. When malicious traffic is detected, it can perform real-time blocking operations, such as cutting off abnormal connections, dropping malicious packets, blocking attack IP addresses and so on, without waiting for administrator's intervention. For example, when IPS identifies the transmission of an email attachment with the characteristics of a ransomware virus, it will immediately intercept the email to prevent the virus from entering the internal network. In the face of DDoS attacks, it can filter out a large number of fake requests and ensure the normal operation of the server.
The defense capability of IPS relies on "real-time response mechanism" and "intelligent upgrade system". Modern IPS regularly updates the attack signature database to synchronize the latest hacker attack methods. Some high-end products also support "behavior analysis and learning", which can automatically identify new and unknown attacks (such as zero-day exploits). An IPS system used by a financial institution found and blocked a SQL injection attack using an undisclosed vulnerability by analyzing the abnormal database query frequency, preventing the tampering of core transaction data.
Although IDS and IPS have similar functions, there are key differences: from the perspective of role, IDS is "passive monitoring + alerting", and does not directly intervene in network traffic. It is suitable for scenarios that need a full audit but do not want to affect the service. IPS stands for "active Defense + Intermission" and can intercept attacks in real time, but it must ensure that it does not misjudge normal traffic (false positives can cause service disruptions). In practical applications, they often "cooperate" -- IDS is responsible for monitoring and retaining evidence comprehensively to supplement attack signatures for IPS. IPS is responsible for real-time interception, defense threats, reducing losses caused by attacks, and forming a complete security closed loop of "detection-defense-traceability".
IDS/IPS plays an important role in different scenarios: in home networks, simple IPS capabilities such as attack interception built into routers can defend against common port scans and malicious links; In the enterprise network, it is necessary to deploy professional IDS/IPS devices to protect internal servers and databases from targeted attacks. In cloud computing scenarios, cloud-native IDS/IPS can adapt to elastically scalable cloud servers to detect abnormal traffic across tenants. With the continuous upgrading of hacker attack methods, IDS/IPS is also developing in the direction of "AI intelligent analysis" and "multi-dimensional correlation detection", further improving the defense accuracy and response speed of network security.
Mylinking™ Network Packet Brokers application in Intrusion Prevention System (IPS)
Post time: Oct-22-2025