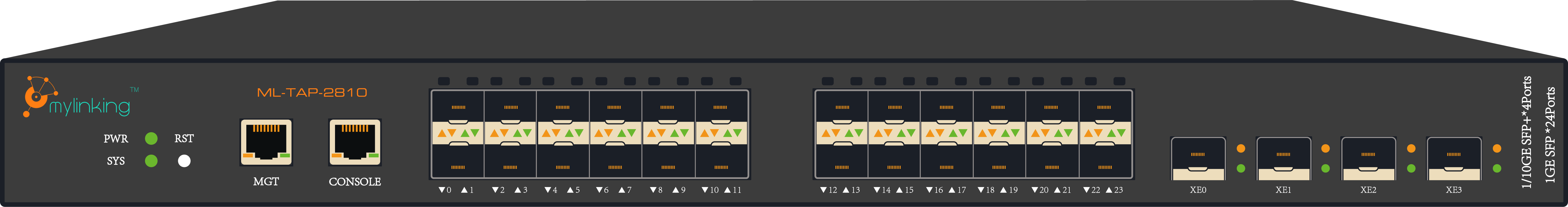
The Network Packet Broker (NPB), which includes the commonly used 1G NPB, 10G NPB, 25G NPB, 40G NPB, 100G NPB, 400G NPB, and Network Test Access Port (TAP), is a hardware device that plugs directly into the network cable and sends a piece of network communication to other devices.
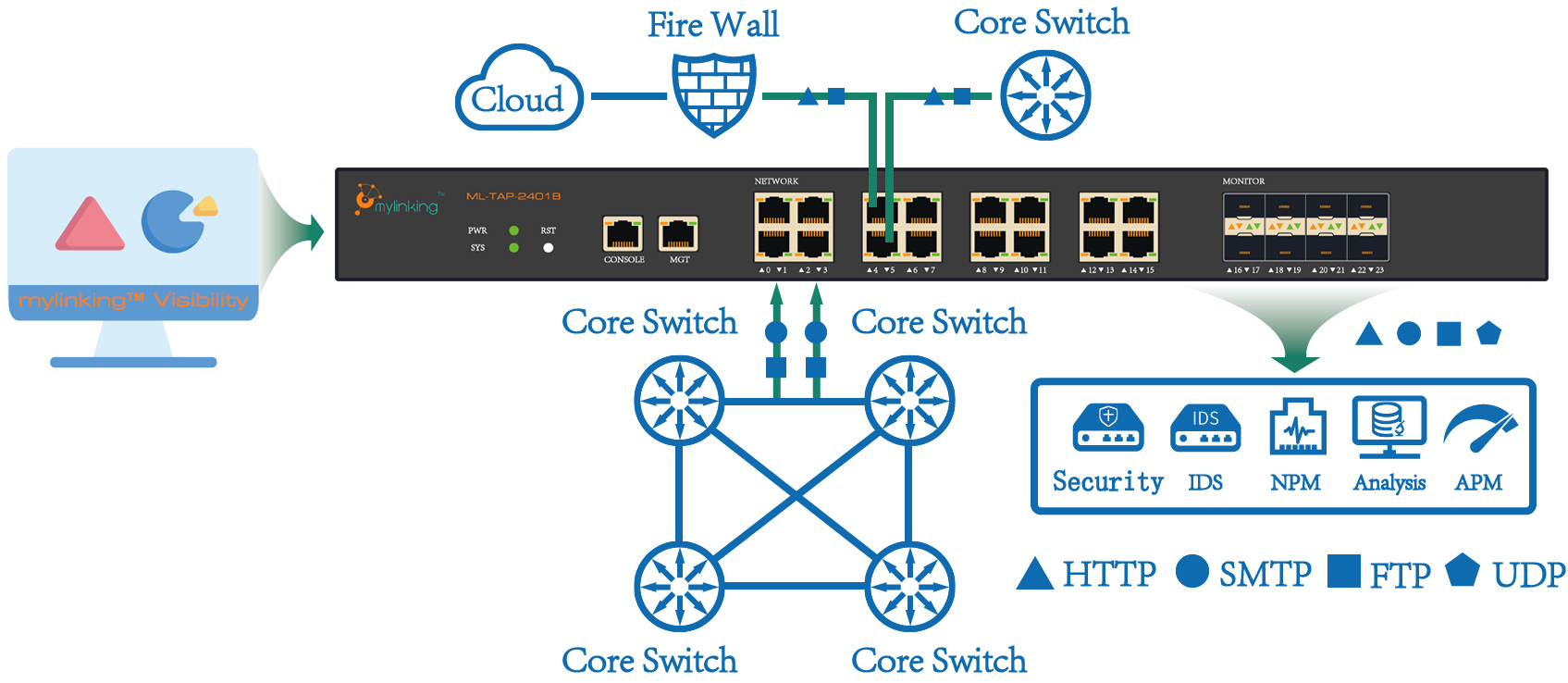
Network Packet Brokers are commonly used in network intrusion detection systems (IDS), network detectors, and profilers. Port mirroring session. In shunting mode, the monitored UTP link (unmasked link) is divided into two parts by a TAP shunting device. The shunted data is connected to the collection interface to collect data for the Internet information security monitoring system.
What does Network Packet Broker(NPB) do for you?
Key Features:
1. Independent
It is an independent piece of hardware and does not affect the load of existing network devices, which has great advantages over port mirroring.
It is an in-line device, which simply means that it needs to be wired into a network. However, this also has the disadvantage of introducing a point of failure, and because it is an online device, the current network needs to be interrupted at deployment time, depending on where it is deployed.
2. Transparent
Transparent means the pointer to the current network. After accessing the network shunt, it has no impact on all devices in the current network, and is completely transparent to them. Of course, this also includes the traffic sent by the network shunt to the monitoring device, which is also transparent to the network.
Working principle:
The traffic shunting(distribtion) based on input data, replicate, gathering, filtering, 10G POS data transformation through the protocol conversion to tens of megabytes LAN data, according to the specific algorithm for load balancing output, the output at the same time to ensure that all the packets of the same session, or the same IP output all the packets from the same user interface.
Functional Features:
1. Protocol conversion
The mainstream Internet data communication interfaces used by ISPs include 40G POS, 10G POS/WAN/LAN, 2.5G POS, and GE, while the data receiving interfaces used by application servers are GE and 10GE LAN interfaces. Therefore, the protocol conversion usually mentioned on Internet communication interfaces mainly refers to the conversion between 40G POS, 10G POS, and 2.5G POS to 10GE LAN or GE, and the bidirectional cotransfer between 10GE WAN and 10GE LAN and GE.
2. Data collection and distribution.
Most data collection applications basically extract the traffic they care about and discard the traffic they don't care about. The data traffic of a specific IP address, protocol, and port is extracted by five-tuple (source IP address, destination IP address, source port, destination port, and protocol) convergence. When output, the same source, same location and load balance output are ensured according to the specific HASH algorithm.
3. Feature code filtering
For P2P traffic collection, the application system may only focus on some specific traffic, such as streaming media PPStream, BT, Thunderbolt, and the common keywords on HTTP such as GET and POST, etc. The feature code matching method can be used for extraction and convergence. The diverter supports fixed-position feature code filtering and floating feature code filtering. A floating feature code is an offset specified on the basis of a fixed location feature code. It is suitable for applications that specify the feature code to be filtered, but do not specify the specific location of the feature code.
4. Session management
Identifies session traffic and flexibly configures the session forwarding N value (N=1 to 1024). That is, the first N packets of each session are extracted and forwarded to the back-end application analysis system, and the packets after N are discarded, saving resource overhead for the downstream application analysis platform. In general, when you use IDS to monitor events, you do not need to process all the packets of the entire session; instead, you simply need to extract the first N packets of each session to complete the event analysis and monitoring.
5. Data mirroring and replication
The splitter can realize the mirroring and replication of the data on the output interface, which ensures the data access of multiple application systems.
6. 3G network data acquisition and forwarding
The data collection and distribution on 3G networks are different from traditional network analysis modes. Packets on 3G networks are transmitted on backbone links through multiple layers of encapsulation. Packet length and encapsulation format are different from those of packets on common networks. The splitter can accurately identify and process tunnel protocols such as GTP and GRE packets, multilayer MPLS packets, and VLAN packets. It can extract IUPS signaling packets, GTP signaling packets, and Radius packets to specified ports based on packet characteristics. In addition, it can divide packets according to the inner IP address. Support for oversized packages (MTU> 1522 Byte) processing, can perfectly realize the 3G network data collection and shunt application.
Feature Requirements:
- Supports traffic distribution by L2-L7 application protocol.
- Supports 5-tuple filtering by exact source IP address, destination IP address, source port, destination port, and protocol and with a mask.
- Supports output load balancing and output homology and homology.
- Supports filtering and forwarding by character strings.
- Supports session management. Forward the first N packets of each session. The value of N can be specified.
- Supports for multiple users. The data packets matching the same rule can be provided to a third party at the same time, or the data on the output interface can be mirrored and replicated, ensuring the data access of multiple application systems.
Financial Industry Solution Solution Advantage Solution
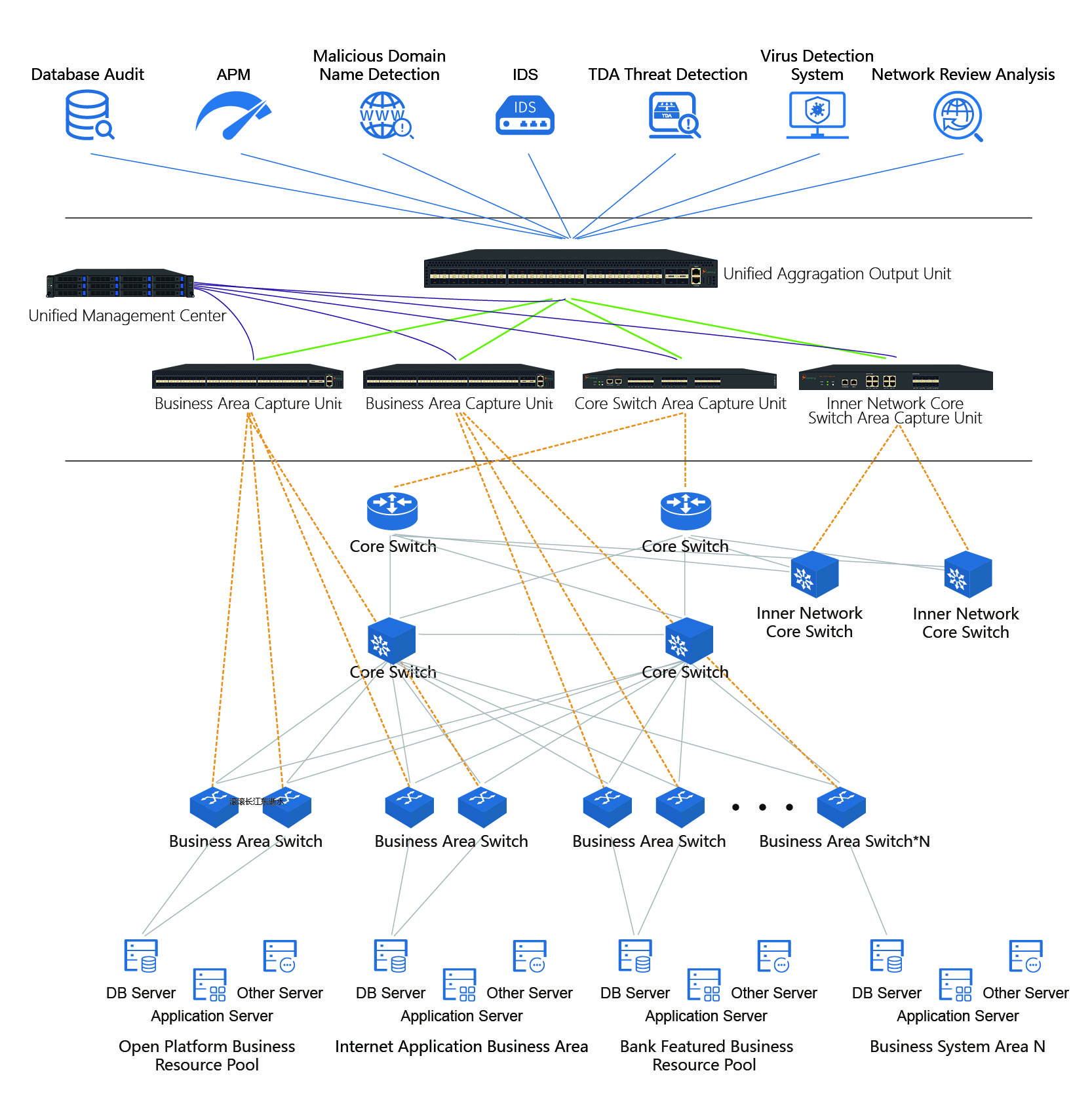
With the rapid development of global information technology and the deepening of informatization, the scale of enterprise network has been gradually expanded, and the dependence of various industries on information system has become increasingly high. At the same time, the enterprise network of internal and external attack, irregularities, and information security threats are also growing, with large quantities of network protection, application business monitoring system put into operation in succession, all sorts of business monitoring, safety protection equipment deployed throughout the network, there will be a waste of information resources, monitor the blind spot, repeated monitoring, network topology and disorderly problem such as unable to effectively obtain the target data, leading to monitor equipment low working efficiency, high investment, low income, the late maintenance and management difficulties, data resources is difficult to control.
Post time: Sep-08-2022