What is the Bypass?
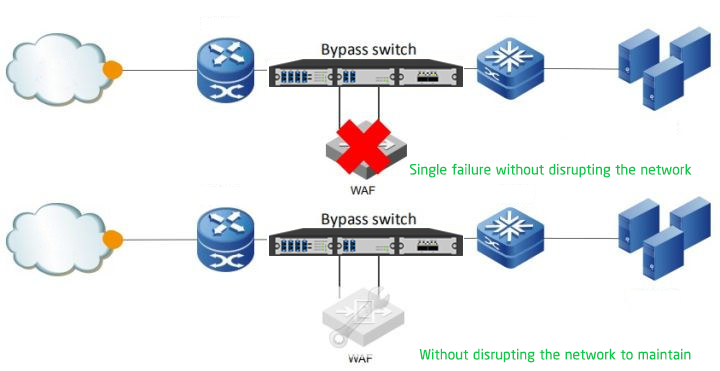
The Network Security Equipment is commonly used in between two or more networks, such as between internal network and external network. The Network Security Equipment through its network packet analysis, to determine whether there is a threat, after processed according to certain routing rules to forward the packet to go out, and if the network security equipment malfunctioned, For example, after a power failure or crash, network segments connected to the device are disconnected from each other. In this case, if each network needs to be connected each other, then Bypass must appear.
The Bypass function, as the name implies, enables the two networks physically connect without passing through the system of the network security device through a specific triggering state (power failure or crash). Therefore, when the network security device fails, the network connected to the Bypass device can communicate with each other. Of course, the network device does not process packets on the network.
How classify the Bypass Application Mode?
Bypass is divided into control or trigger modes, which are as follows
1. Triggered by power supply. In this mode, the Bypass function enable when the device powered off. If the device powered on, the Bypass function will be disabled immediately.
2. Controlled by GPIO. After logging in to the OS, you can use GPIO to operate specific ports to control the Bypass switch.
3. Control by Watchdog. This is an extension of mode 2. You can use the Watchdog to control the enabling and disabling of the GPIO Bypass program to control the Bypass status. In this way, if the platform crashes, the Bypass can be opened by Watchdog.
In practical applications, these three states often exist at the same time, especially the two modes 1 and 2. The general application method is: when the device is powered off, the Bypass is enabled. After the device powered on, the Bypass is enabled by the BIOS. After the BIOS takes over the device, the Bypass is still enabled. Turn off the Bypass so that the application can work. During the entire startup process, there is almost no network disconnection.
What is the Principle of Bypass implementation?
1. Hardware Level
At the hardware level, relays are mainly used to achieve Bypass. These relays are connected to signal cables of the two Bypass network ports. The following figure shows the working mode of the relay using one signal cable.
Take the power trigger as an example. In the case of power failure, the switch in the relay will jump to the state of 1, that is, Rx on the RJ45 interface of LAN1 will directly connect to RJ45 Tx of LAN2, and when the device is powered on, the switch will connect to 2. In this way, if the network communication between LAN1 and LAN2 is required, You need to do that through an application on the device.
2. Software Level
In the classification of Bypass, GPIO and Watchdog are mentioned to control and trigger the Bypass. In fact, both of these two ways operate the GPIO, and then the GPIO controls the relay on the hardware to make the corresponding jump. Specifically, if the corresponding GPIO is set to high level, the relay will jump to position 1 correspondingly, whereas if the GPIO cup is set to low level, the relay will jump to position 2 correspondingly.
For Watchdog Bypass, it is actually added Watchdog control Bypass on the basis of GPIO control above. After the watchdog takes effect, set the action to bypass on the BIOS. The system activates the watchdog function. After the watchdog takes effect, the corresponding network port bypass is enabled and the device enters the bypass state. In fact, the Bypass is also controlled by GPIO, but in this case, the writing of low levels to GPIO is performed by the Watchdog, and no additional programming is required to write GPIO.
The hardware Bypass function is a mandatory function of network security products. When the device is powered off or crashed, the internal and external ports are physically connected to form a network cable. In this way, data traffic can directly pass through the device without being affected by the current status of the device.
High Availability (HA) Application:
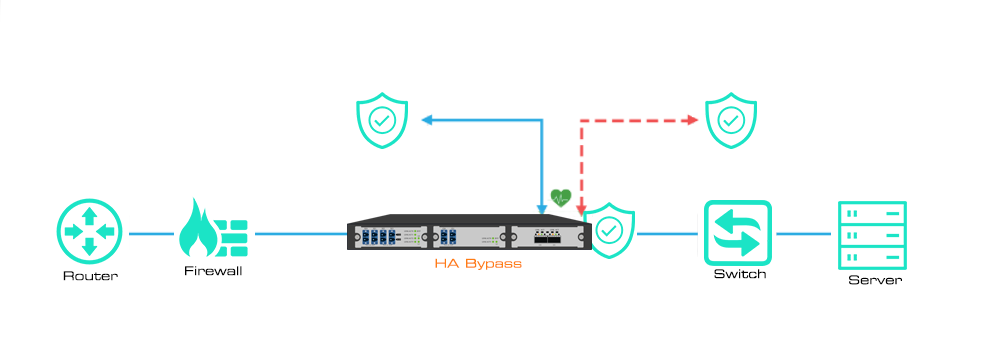
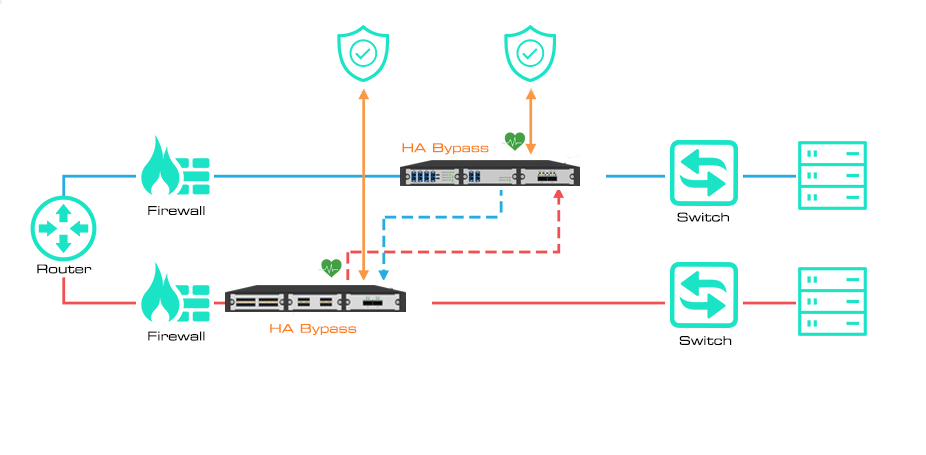
Mylinking™ provide two high availability (HA) solutions, Active/Standby and Active/Active. The Active Standby (or active/passive) deployment to auxiliary tools to provide failover from primary to backup devices. And the Active/Active Deployed to redundant links to provide failover when any Active device fails.
Mylinking™ Bypass TAP supports two redundant inline tools, could be deployed in the Active/Standby solution. One serves as the primary or "Active" device. The Standby or "Passive" device still receives real-time traffic through the Bypass series but is not considered as an inline device. This provides "Hot Standby" redundancy. If the active device fails and the Bypass TAP stops receiving heartbeats, the standby device automatically takes over as the primary device and comes online immediately.
What’s the Advantages you can get based on our Bypass?
1-Allocate traffic before and after the inline tool (such as WAF, NGFW, or IPS) to the out-of-band tool
2-Managing multiple inline tools simultaneously simplifies the security stack and reduces network complexity
3-Provides filtering, aggregation, and load balancing for inline links
4-Reduce the risk of unplanned downtime
5-Failover, high availability [HA]
Post time: Dec-23-2021