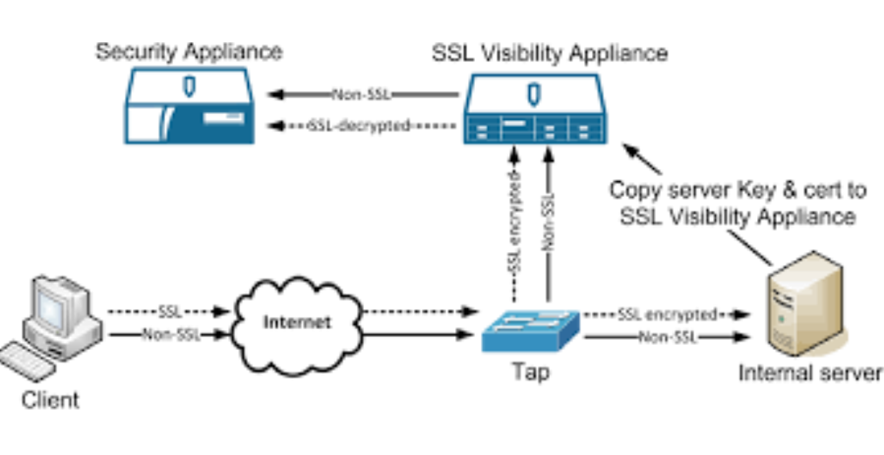
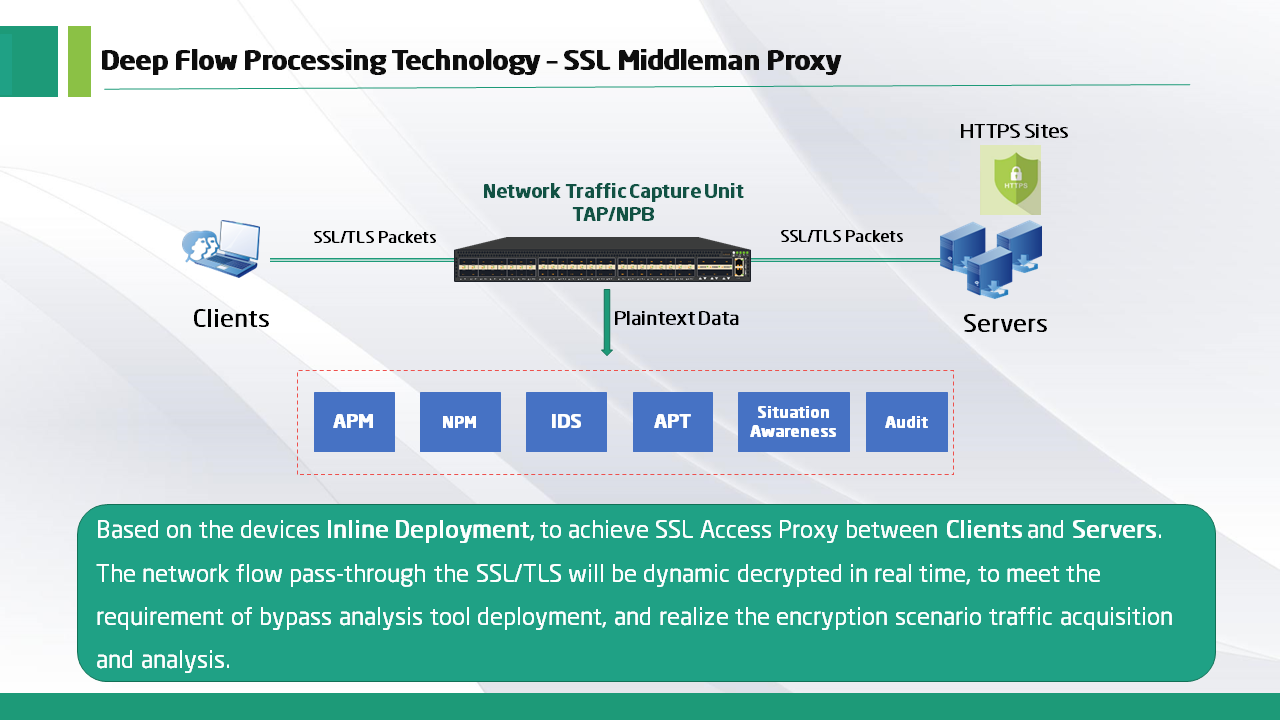
What is the SSL/TLS Decryption?
SSL decryption, also known as SSL/TLS decryption, refers to the process of intercepting and decrypting Secure Sockets Layer (SSL) or Transport Layer Security (TLS) encrypted network traffic. SSL/TLS is a widely used encryption protocol that secures data transmission over computer networks, such as the internet.
SSL decryption is typically performed by security devices, such as firewalls, intrusion prevention systems (IPS), or dedicated SSL decryption appliances. These devices are placed strategically within a network to inspect encrypted traffic for security purposes. The primary objective is to analyze the encrypted data for potential threats, malware, or unauthorized activities.
To perform SSL decryption, the security device acts as a man-in-the-middle between the client (e.g., web browser) and the server. When a client initiates an SSL/TLS connection with a server, the security device intercepts the encrypted traffic and establishes two separate SSL/TLS connections—one with the client and one with the server.
The security device then decrypts the traffic from the client, inspects the decrypted content, and applies security policies to identify any malicious or suspicious activity. It may also perform tasks such as data loss prevention, content filtering, or malware detection on the decrypted data. Once the traffic has been analyzed, the security device re-encrypts it using a new SSL/TLS certificate and forwards it to the server.
It's important to note that SSL decryption raises privacy and security concerns. Since the security device has access to the decrypted data, it can potentially view sensitive information such as usernames, passwords, credit card details, or other confidential data transmitted over the network. Therefore, SSL decryption is generally implemented within controlled and secured environments to ensure the privacy and integrity of the intercepted data.
SSL Decryption has three common modes, they are:
- Passive Mode
- Inbound Mode
- Outbound Mode
But, what're the differences of three modes of SSL Decryption?
|
Mode |
Passive Mode |
Inbound Mode |
Outbound Mode |
|
Description |
Simply forwards SSL/TLS traffic without decryption or modification. |
Decrypts client requests, analyzes and applies security policies, then forwards the requests to the server. |
Decrypts server responses, analyzes and applies security policies, then forwards the responses to the client. |
|
Traffic Flow |
Bi-directional |
Client to Server |
Server to Client |
|
Device Role |
Observer |
Man-in-the-Middle |
Man-in-the-Middle |
|
Decryption Location |
No decryption |
Decrypts at the network perimeter (usually in front of the server). |
Decrypts at the network perimeter (usually in front of the client). |
|
Traffic Visibility |
Encrypted traffic only |
Decrypted client requests |
Decrypted server responses |
|
Traffic Modification |
No modification |
May modify traffic for analysis or security purposes. |
May modify traffic for analysis or security purposes. |
|
SSL Certificate |
No need for private key or certificate |
Requires private key and certificate for the server being intercepted |
Requires private key and certificate for the client being intercepted |
|
Security Control |
Limited control as it cannot inspect or modify encrypted traffic |
Can inspect and apply security policies to client requests before reaching the server |
Can inspect and apply security policies to server responses before reaching the client |
|
Privacy Concerns |
Does not access or analyze encrypted data |
Has access to decrypted client requests, raising privacy concerns |
Has access to decrypted server responses, raising privacy concerns |
|
Compliance Considerations |
Minimal impact on privacy and compliance |
May require compliance with data privacy regulations |
May require compliance with data privacy regulations |
Compared with the serial decryption of secure delivery platform, the traditional serial decryption technology has limitations.
Firewalls and network security gateways that decrypt SSL/TLS traffic often fail to send decrypted traffic to other monitoring and security tools. Similarly, load balancing eliminates SSL/TLS traffic and perfectly distributes the load among the servers, but it fails to distribute the traffic to multiple chaining security tools before re-encrypting it. Finally, these solutions lack control over traffic selection and will distribute unencrypted traffic at wire-speed, typically sending the entire traffic to the decryption engine, creating performance challenges.
With Mylinking™ SSL decryption, you can solve these problems:
1- Improve existing security tools by centralizing and offloading SSL decryption and re-encryption;
2- Expose hidden threats, data breaches, and malware;
3- Respect data privacy compliance with policy-based selective decryption methods;
4 -Service chain multiple traffic intelligence applications such as packet slicing, masking, deduplication, and adaptive session filtering, etc.
5- Affect your network performance, and make appropriate adjustments to ensure a balance between security and performance.
These are some of the key applications of SSL decryption in network packet brokers. By decrypting SSL/TLS traffic, NPBs enhance the visibility and effectiveness of security and monitoring tools, ensuring comprehensive network protection and performance monitoring capabilities. SSL decryption in network packet brokers (NPBs) involves accessing and decrypting encrypted traffic for inspection and analysis. Ensuring the privacy and security of the decrypted traffic is of utmost importance. It's important to note that organizations deploying SSL decryption in NPBs should have clear policies and procedures in place to govern the use of decrypted traffic, including access controls, data handling, and retention policies. Compliance with applicable legal and regulatory requirements is essential to ensure the privacy and security of decrypted traffic.
Post time: Sep-04-2023